Introduction
As Saudi Arabia modernizes under Vision 2030, industries are facing rising demands for operational excellence, sustainability, and digital readiness. One key factor driving this transformation is Preventive Maintenance (PM)—a proactive approach that ensures assets and systems are maintained before failures occur.
While many sectors still rely on reactive maintenance, the shift toward preventive and predictive strategies is gaining momentum. This article explores the current landscape, key benefits for major Saudi industries, and the future of maintenance in a digitally connected economy.
1. What Is Preventive Maintenance?
Preventive Maintenance involves scheduled inspections, servicing, and minor repairs to keep equipment and infrastructure running efficiently. Instead of reacting to breakdowns, PM aims to prevent them entirely saving time, money, and downtime.
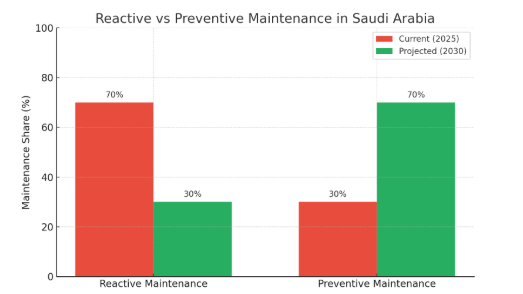
2. Maintenance Trends in Saudi Arabia
Many facilities across Saudi Arabia—especially older or government-owned assets—still operate under reactive maintenance models, where action is only taken after something breaks.
Key Observations:
-
Around 70% of maintenance activities are still reactive
-
Unplanned equipment failures cause up to 30% operational downtime
-
Limited CMMS and asset tracking adoption in small to mid-sized operations
These gaps present a major opportunity for industries to adopt structured PM programs, reduce costs, and optimize long-term performance.
3. Industry-Specific Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance delivers clear value across various Saudi industries:
Manufacturing & Industrial Plants
-
Reduces unplanned production halts
-
Improves machine lifespan and product quality
-
Lowers emergency repair and spare part costs
Healthcare & Hospitals
-
Ensures life-critical systems (oxygen, HVAC, backup power) operate reliably
-
Supports MOH regulatory compliance and inspection readiness
-
Enhances patient safety and operational continuity
Commercial Real Estate & Facility Management
-
Prevents elevator, AC, and water system breakdowns
-
Enhances tenant satisfaction through consistent performance
-
Reduces utility costs through energy-efficient equipment
Logistics, Warehousing & Retail
-
Maintains cold storage and climate-controlled environments
-
Ensures equipment uptime for 24/7 operations
-
Prevents spoilage and delays in supply chains
4. Future Outlook: Smart Maintenance by 2030
As the Kingdom continues to develop smart cities and giga-projects, the future of maintenance will shift from preventive to predictive.
Key technologies leading this shift include:
-
IoT sensors for real-time performance monitoring
-
CMMS software to automate task scheduling and history tracking
-
AI & analytics to forecast failures before they happen
-
Digital twins that simulate asset behavior and optimize planning
By 2030, it is expected that over 70% of facility maintenance in major developments will be either preventive or predictive, driven by sustainability, efficiency, and compliance goals.
5. Challenges to Implementation
Despite the benefits, several challenges exist:
-
Lack of trained FM and technical personnel
Many maintenance teams in older facilities or remote areas lack formal training in preventive practices, modern tools, or diagnostic techniques. This limits their ability to shift from reactive to proactive models.
-
Limited integration of CMMS in public-sector facilities
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are not widely adopted across public buildings due to outdated systems, manual processes, or lack of digital infrastructure.
-
Budget prioritization focused on reactive problem-solving
Budgets are often allocated toward fixing visible issues after breakdowns rather than investing in long-term preventive strategies—mainly due to short-term thinking or limited data on lifecycle costs.
-
Resistance to change from traditional maintenance practices
Some facility teams, contractors, or decision-makers are used to reactive routines and may resist changing workflows, retraining staff, or adopting digital tools unless mandated.
Addressing these issues requires investment in digital tools, workforce upskilling, and strategic FM partnerships.
Conclusion
Preventive maintenance is not just about keeping systems running—it’s about creating smarter, more efficient, and future-ready operations. As Saudi Arabia positions itself as a leader in smart infrastructure, PM becomes essential for any industry seeking resilience, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
The transition from reactive to preventive—and ultimately predictive—maintenance is not a luxury, but a necessity in the Kingdom’s journey toward Vision 2030.
References
- MaintWorld, Why Preventative Maintenance Is a Vital Part of Any Businesses Maintenance Strategy, 21 August 2023. Available at: https://www.maintworld.com/Partner-Articles/Why-Preventative-Maintenance-is-a-Vital-Part-of-Any-Businesses-Maintenance-Strategy





