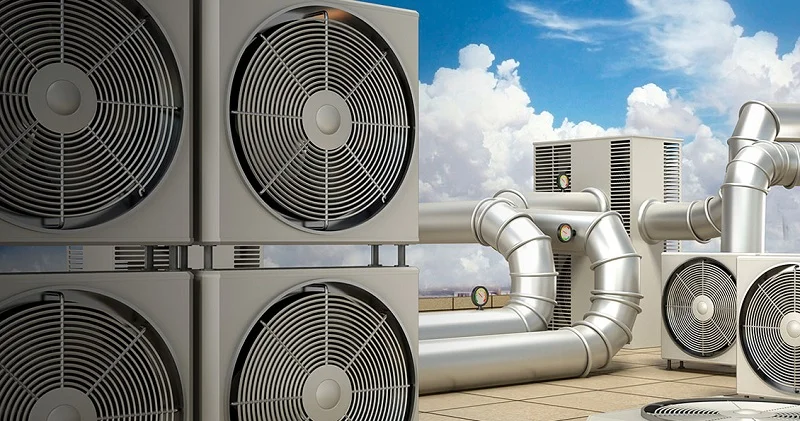
When most people hear about HVAC building systems, they usually think of air conditioning. But in facility management, climate control is far more than just cooling. It involves a complex network of technologies that ensure safe, healthy, and energy-efficient environments across industrial, commercial, and residential buildings.
In this post, we’ll explore the true depth of environmental control in modern facility management — its components, types, and how integrated strategies can reduce operational costs while improving indoor comfort.
With Vision 2030 accelerating digital transformation in Saudi Arabia, today’s FM teams are expected to optimize these systems not just for performance and reliability, but also for sustainability and regulatory compliance. A modern approach to environmental systems is no longer optional — it’s a strategic necessity.
What Is HVAC in Facility Management?
HVAC = Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning — a system designed to maintain indoor climate conditions suitable for both people and processes.
In facility management, this system is no longer a luxury — it’s a critical part of the building’s operational infrastructure that directly impacts:
-
Health & safety of occupants (indoor air quality, humidity control)
-
Equipment performance (such as in server rooms and cleanrooms)
-
Energy cost control (accounting for up to 50% of energy use in some facilities)
-
Regulatory compliance (SASO, ASHRAE, Ministry of Health guidelines)
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring occupant comfort and system efficiency. A failure in any area can lead to increased energy consumption, operational disruption, or even health risks.
Johnson Controls: Understanding HVAC Component https://www.johnsoncontrols.com/hvac-equipment
Key Components in HVAC Systems
Understanding the full ecosystem helps FM teams ensure performance, safety, and compliance:
Component: Air Handling Units (AHUs)
Description: Condition and circulate air, especially in large buildings
Component: Chillers & Boilers
Description: Core units for centralized cooling/heating
Reference:https://www.trane.com/commercial/north-america/us/en/products-systems/chillers.html
Component: Fan Coil Units (FCUs)
Description: Smaller terminal units connected to AHUs
Component: Variable Air Volume (VAV) Boxes
Description: Adjust air supply in zones to save energy
Component: VRF/VRV Units
Description: Advanced systems with dynamic zoning and energy optimization
Reference: https://www.mitsubishicomfort.com/vrf
Component: Thermostats, Sensors & Controls
Description: Smart automation of temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels
Reference: https://www.energystar.gov/products/heating_cooling/smart_thermostats
Component: Ductwork
Description: Channels to distribute air efficiently across zones
Reference: https://www.trane.com/commercial/north-america/us/en/products-systems/building-controls.html
Types of HVAC Systems Used in FM
Facilities differ in usage, size, and energy demands. HVAC systems must be selected accordingly:
1. Centralized HVAC Systems
-
Found in: Malls, Airports, Hospitals, Mega-factories
-
Features: Central chillers, extensive ducting, controlled via BMS
-
Pros: Scalable, efficient, stable for large loads
2. Split and Multi-Split Systems
-
Found in: Offices, Schools, Clinics
-
Pros: Simple to install, flexible for zone control
3. VRF/VRV Systems
-
Found in: Hotels, Corporate Towers, Luxury Apartments
-
Features: Simultaneous cooling/heating in different zones
-
Pros: High energy savings, smart zoning, minimal ductwork
Reference: https://www.daikin.com/products/ac/lineup/vrv
4. Packaged Rooftop Units
-
Found in: Warehouses, Supermarkets, Gyms
-
Features: All-in-one system, roof-mounted
-
Pros: Space-saving, reliable, easy to maintain
Reference: https://www.carrier.com/commercial/en/us/products/packaged-outdoor/
5. Ductless Mini-Split Systems
-
Found in: Renovation projects, heritage buildings
-
Pros: No ducting needed, quiet, individual zone control
The Facility Management Perspective on HVAC
In the world of FM, HVAC systems are no longer treated as isolated mechanical equipment. Instead, they are considered strategic assets that affect:
-
Building energy consumption
-
Health and safety standards
-
Tenant satisfaction and productivity
-
Equipment uptime in temperature-sensitive areas (e.g., server rooms)
By implementing robust HVAC strategies, FM teams can significantly lower costs, reduce environmental impact, and improve operational continuity.
Modern HVAC systems are now data-driven and AI-enabled, allowing real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance — part of the broader shift toward AI-driven facility management in Saudi Arabia. for a deeper understanding of how AI is shaping the future of facility operations in the Kingdom, read our detailed article:
Smart HVAC: Technology and Integration
The next generation of HVAC systems is all about smart integration. Facility managers now use technologies such as:
-
Building Management Systems (BMS) for centralized control
-
IoT Sensors to track air quality, equipment health, and occupancy
-
Predictive Maintenance to prevent failures before they happen
-
Energy Optimization Software for cost-effective scheduling
These technologies provide real-time insights and improve both energy efficiency and response time for troubleshooting.
Referrenec: https://new.siemens.com/global/en/products/buildings/automation.html
Benefits of Effective HVAC Management in FM
-
Operational Stability: Maintains safe and comfortable working environments
-
Cost Efficiency: Reduces energy bills through automation and optimization
-
Risk Prevention: Minimizes chances of equipment failure and air quality issues
-
Compliance: Helps meet government and international environmental standards
-
Sustainability: Supports green building goals by minimizing energy waste
The Cost of Ignoring HVAC in Facility Management
Poor HVAC maintenance leads to:
-
Unnecessary equipment failures
-
Increased energy costs
-
Regulatory violations
-
Unhealthy indoor environments
Regular inspections, digital monitoring, and proactive repairs are essential to avoid these pitfalls.
Conclusion: Why HVAC Is a Strategic FM Priority
This is no longer just about heating or cooling. It is a core building system tied to cost savings, occupant health, and regulatory compliance. Whether you’re managing a hospital, warehouse, office tower, or university campus — your approach to will directly affect your facility’s performance and longevity.
Smart facility management means thinking beyond the AC unit — and embracing as a strategic enabler of building efficiency, comfort, and sustainability.